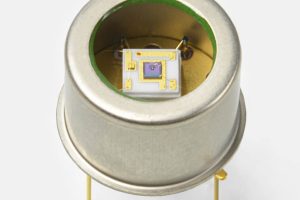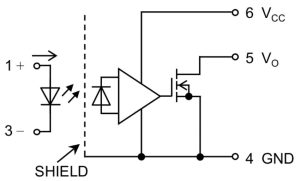
They are amplified types with threshold detection and an open-drain output.
Operation is across -40 to +125°C and the secondary side will run from between 2.7 and 5.5V, consuming ~1mA. Operation is specified at 3.3 and 5V.
Input-referred hysteresis is typically 200μA, but absolute levels are not tightly controlled within 0.5 to 5mA. The device is specified with inputs of 7.5 or 10mA.
Output pull-down voltage depends on number of factors, but it take 16mA below 0.3V in most circumstances. A 350Ω resistor to 3.3V or 5V is used for data sheet timing measurements.
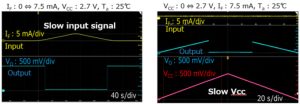 A form of under-voltage lock-out is implemented to prevent output chattering if the power supply rises or falls slowly, said Toshiba, which provided Electronics Weekly with the diagram on the left – although the characteristic does not appear to be specified in the data sheet at the time of writing.
A form of under-voltage lock-out is implemented to prevent output chattering if the power supply rises or falls slowly, said Toshiba, which provided Electronics Weekly with the diagram on the left – although the characteristic does not appear to be specified in the data sheet at the time of writing.
An internal an internal Faraday shield raises common-mode transient immunity of to ±50kV/µs, and they are compliant with IEC 61131-2 (Type 1).

The four parts are:
- TLP2362B 10Mbit/s, 3,75kVrms isolation, 3.7 x 7mm SO6
- TLP2368B 20Mbit/s, 3,75kVrms isolation, 3.7 x 7mm SO6
- TLP2762B 10Mbit/s, 5kVrms isolation, 3.84 x 10mm SO6L
- TLP2768B 20Mbit/s, 5kVrms isolation, 3.84 x 10mm SO6L
20Mbit/s parts have a propagation delay <60ns, which increases to <100ns in 10MHz types. All are 2.3mm tall.
There is a tiny bit more on the power supply hysteresis on this web page and IEC 61131-2 (Type 1) inputs in this document
 Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News
Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News