We're talking about Chinese unicorns, the state of the chip industry, use of electrostatic-hydraulic actuators in robotics, and Ofcom's view of Project Kuiper...
Tag Archives: actuator
Electro-hydraulic actuators make a nimble leg
Electro-hydraulic muscles are sometimes a viable alternative to electric motors in robot legs, according to researchers at Max Planck ETH Center for Learning Systems. This sort of electricity-to-movement transducer uses a liquid-filled bag with electrodes on opposite faces. A high potential difference across the electrodes pulls them together, squashing the liquid out of the way – and that action can ...
Sponsored content: Extended assortment of Mean Well products
Over the last decades, Mean Well has become one of the most recognisable global providers of power supply modules and converters. However, its product range also includes a broad selection of other solutions, such as KNX equipment for building automation systems. The assortment described below includes modules compatible with the KNX system, i.e. a standard applied in home and industrial ...
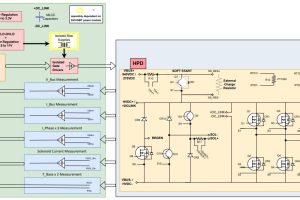
15kVA three-phase motor drives for more-electric aircraft
Microchip is aiming at 15kVA actuators in more-electric aircraft with a pair of three-phase power drive assemblies with silicon carbide power components. Both consists of a power module soldered to driver board “The companion gate driver boards are designed to be integrated with [power] modules to provide an all-in-one motor drive solution for the electrification of systems such as flight ...
Robotic soft actuators stay strong
A happy accident has revealed a way to stop electrostatic soft actuators from going limp. These actuators consists of a flat plastic bag of dielectric liquid with electrodes on opposite faces of the bag. Max Planck ETH Center for Learning Systems made a nimble leg from similar actuators in 2024 If a high potential difference is placed between the two ...
Soft gripper weighs 130g, lifts 100kg
Korean engineers and scientists have developed a soft gripper that can be used to lift 100kg, while weighing only 130g. The device is inspired by weaving and can be made at different sizes, always maintaining large ratio between gripping capacity and its own mass. “Utilising soft, flexible materials such as cloth, paper and silicone, soft robotic grippers acts like a ...
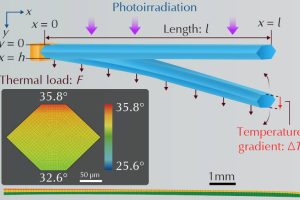
Photothermal resonance for micro-actuators?
Researchers in Japan have exploited resonance to get large amplitude motion from rod-like microcrystals, in a way that could be useful in soft robotics according to Waseda University. Using UV light, they set out to bend a particular type of 2,4-dinitroanisole crystals – chosen because of their large thermal expansion coefficient. The UV wavelength selected matches an absorption peak in ...
NEMA 6 linear actuator is only 14mm across
Nanotec has introduced its first linear actuator with a NEMA 6 stepper motor – the flange is only 14mm across. “This compact unit is ideal for applications with space restrictions, such as medical or analytical instruments, or lab automation and optical applications,” according to the company. Called LSA14, there are two versions; Acme and trapezoidal (see table below), with the ...
Auto-focus and image stabilisation in the same shape memory actuator
Cambridge Mechatronics has created a shape memory alloy actuator for cameras that combines auto-focus and optical image stabilisation (AF+OIS) in the same structure. Designed to move the lens above an image sensor, the actuator uses eight shape memory wires. “By placing shape memory alloy wires in a three-dimensional configuration around the lens, the single actuator can perform both OIS and ...
Electrostatic actuators improved by self-polarising ferroelectrics
Electrostatic actuators that work at lower voltages could come out of research at the Tokyo Institute of Technology. These devices consist of two oppositely charged electrodes that generate a force when there is an electric field between them. “By altering the shape of their electrodes and filling the gap between them with flexible, soft materials, various configurations for electrostatic actuators ...
 Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News
Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News