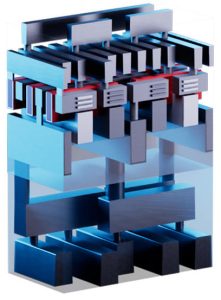
“The PDK will enable virtual digital designs in imec’s N2 technology, including backside power delivery network,” according to the Belgion semiconductor research lab. “This will give academia and industry the tools to train the semiconductor experts of tomorrow and enable the industry to transition their products into next generations technologies through meaningful design pathfinding.”
Intended to be embedded in EDA tool suites, such as from Cadence Design Systems and Synopsys, it is being offered with a concomitant training program offered through EuroPractice – the training program is scheduled to start early in Q2, hands-on with Cadence and the Synopsys software.
Pathfinding?
Imec explained how its pathfinding kit relates to normal PDKs:
Foundry PDKs give chip designers access to a library of tested and proven components to deliver functional and reliable designs. These are usually available to the ecosystem once the technology reaches a critical level of manufacturability. However, restricted access and the need for NDAs have created a high threshold for academia and industry to access advanced technology nodes during their development. Access to imec N2 PDK will help both academia and commercial companies.
Infrastructure for digital design is included, based on a set of digital standard cell libraries and SRAM IP macros, and there are plans to extend the pathfinding platform to more advanced nodes – A14, for example.
 Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News
Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News


