Orange and Vodafone have agreed to share O-RAN networks in Europe, with RAN sharing in rural areas where they both have mobile networks.
The first commercial sites to be deployed under this agreement are planned to start this year in a rural area of Romania, near Bucharest.
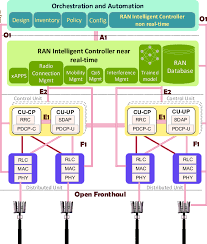
They will provide an initial real-life experience of O-RAN based on the integration of multi-vendor hardware and software.
Orange and Vodafone are currently working to individually select strategic vendors for this initial build phase.
By using open and virtualised RAN, relying on disaggregated software and hardware, Vodafone and Orange will each have greater flexibility when adding new radio sites or upgrading existing ones, while keeping the cost and energy consumption low.
This model will serve as a blueprint to extend 4G and 5G networks to rural communities across Europe.
Under existing sharing agreements one operator is typically responsible for all the component parts of a shared site, with both operators using the same RAN vendor or software release, and life cycle management.
Open RAN sharing paves the way for Orange and Vodafone to reap the benefits of a truly open infrastructure, allowing the sharing of all hardware components (radio units and Cloud infrastructure) while independently managing their own RAN software on a common cloud infrastructure.
As a result, each company can tailor services and capacity to their specific customer needs, while ensuring a strong and secure isolation between each operator’s data.
Testing of the Open RAN solution on a live network will continue throughout 2023, allowing a like-for-like comparison with legacy networks and will aim at confirming the feature and performance parity between Open RAN and traditional RAN solutions, before expanding the Open RAN sharing blueprint to other markets
 Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News
Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News



