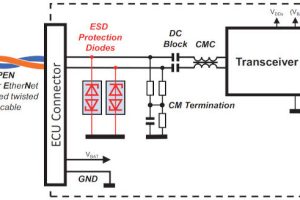
It has been used to create the YQ series of rectifier diodes, available in surface-mount packages from 0.5 x 1mm to TO-263 with ratings between 1A and 30A. Most of them are available with automotive qualification.
Leakage is impressive, with even the biggest (YQ30NL10SEFH) leaking only 150μA (25°C, 100V) and the smallest 6μA. Forward drop at rated current hovers around 0.77V for most of the devices, although ranges across 0.61 to 0.87V.
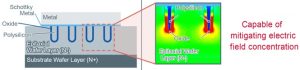
“The trench MOS structure is created by forming a trench using polysilicon in the epitaxial wafer layer to mitigate electric field concentration [left],” according to the company. “This reduces the resistance of the epitaxial wafer layer, achieving lower forward voltage. At the same time, during reverse bias the electric field concentration is minimized, significantly decreasing reverse current.”
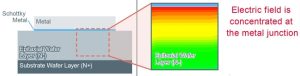
Unlike with typical trench MOS structures where reverse-recovery time is worse than planar types (right) due to larger parasitic capacitance, it continued, the YQ series achieves 15ns by adopting a unique structure.
High-speed switching applications are foreseen in automotive LED headlamps and electric vehicle dc-dc converters.
The full package list is PMDE (2513/1005), SOD-123FL (PMDU 3516/1408), SOD-128 (4725/1910), TO-277A (6546/2618), TO-252AA (10066/3926) and TO-263AB (151101/5940).
Rohm has created an interesting three page application note on the YQ series
 Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News
Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News