“Potential applications range from medical patches and disposable point-of-case testers, to data loggers, smart thermostats, smart locks and sensor inlays,” according to the company.
Called NGC1081, the IC can be temporarily powered by the phone’s NFC field, or more permanently with ~3.3V power supply – a 3V battery, for example.
“Together with its naturally galvanically isolated sensing interface, these features open up countless possibilities for creating sensing use cases that require no batteries and minimal maintenance. This is particularly useful for applications where the power supply needs to be galvanically isolated to meet the safety requirement,” said Infineon.
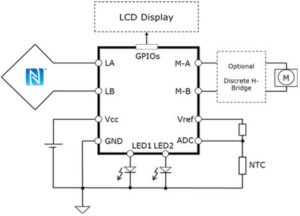
Inside is an Arm Cortex-M0 microcontroller, an ISO14443 type-A NFC front-end, a 250mA 3.6V H-bridge motor driver, a 12bit SAR ADC with four analogue inputs, an analogue output backed by a 10bit DAC, a comparator, a current-to-voltage converter and a thermometer (±0.3°C over 0 to +45°C, ±0.4°C below to -20°C and above to +85°C). There are also eight GPIO pads, some with PWM capability. SPI, I2C and UART interfaces are provided.
The system ROM library contains driver functions to configure and control the H-bridge, and on-die security includes a hardware AES accelerator and a true random number generator.
“The availability of connectivity to mobile phones enables a cloud-based business model,” saidthe company. “This is supported by a mailbox concept that ensures access management and security. Application-specific commands and messages from an open protocol interface can extend the protocol layer.”
Packaging is VQFN-32.
The NGC1081 product page can be found here
Infineon at Embedded World 2023 in Nuremberg – hall 4A stand 138
 Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News
Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News